word2vec 作为一个已经被广为流传的工具,其优点已不必多说。那么它有什么缺陷和不足呢?其实其作者 Mikolov 是一个非常典型的工程型选手,实用主义,什么简单方便有效就用什么;导致 word2vec 作为一个简单的模型,其忽略了很多文本中的其他信息。那么这些其他信息都有什么呢?
word2vec 中考虑的是 linear 的 bag-of-words contexts。这里面,分三点来看:linear、bag-of-words、contexts。linear 强调的就是 plain,没有额外 word-level 以外的信息的,比如 syntax,比如 relation,比如 anything you can imagine;bag-of-words 强调的是 non-ordered,也就是说,词袋模型,这个 word2vec 是没有考虑语序的——会丢失很多信息。第三个是 contexts,一方面是说,word2vec 只能考虑上下文信息(没有考虑词汇内部或者更高的 global/document-level 信息),另一方面是说,这个 contexts 也是被 window size 框住大小的,导致太大的 size computational cost 太大;太小的 size 又不能 handle 足够的信息,同时也会容易出现很多不想出现的词和想出现但没出现的词。
举个这方面论文中的经典例子,比如下面这句话:
“Australian scientist discovers star with telescope”
Note that a context window of size 2 may miss some important contexts (telescope is not a context of discovers), while including some accidental ones (Australian is a context discovers). Moreover, the contexts are unmarked, resulting in discovers being a context of both stars and scientist, which may result in stars and scientists ending up as neighbours in the embedded space. A window size of 5 is commonly used to capture broad topical content, whereas smaller windows contain more focused information about the target word.
就是说,当我们考虑中心词 discover 时,一个常用的窗口大小2,可能就丢失了重要的 telescope 词作为上下文,同时又加入了不相关的 Australian 这个词。这就是一种我们不想要的噪音。因为其实这个窗口的上下文是假设,这些窗口里的词,应该更在 semantic space 中聚合在一起。
所以,后续的研究者们分别从这几个方面(linear、bag-of-words、contexts)做出了改进(虽然他们没有明确说,但我是这样领会精神的)。
(1)linear
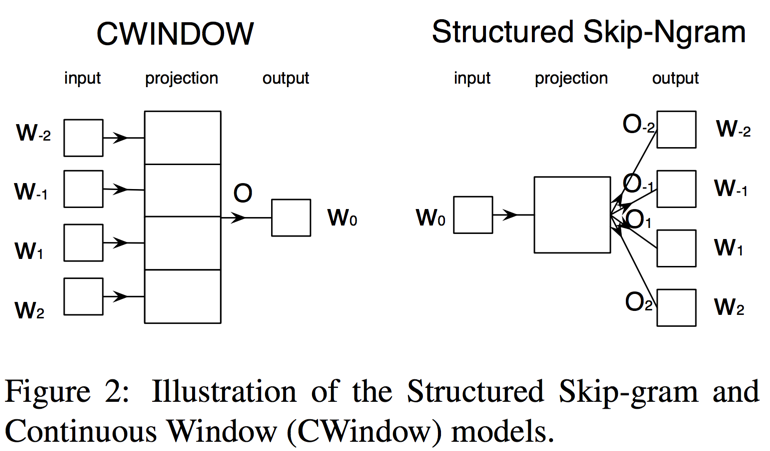
打破 linear 的方法,对于 NLPer 来说,首先就会想到加入 dependency relation,使用已经比较成熟的 dependency parsing(比如 Stanford 的工具),就可以很快引入各种语法树结构,既多了non-linear 的 relation 关系,又有了更多的 tag 作为额外信息,而且还有很顺手的工具包。这方面的工作主要有:
[1] Omer Levy and Yoav Goldberg. 2014. Dependency based word embeddings. In Proceedings of ACL.
[2] Wang Ling, Chris Dyer, Alan Black, and Isabel Trancoso. 2015. Two/too simple adaptations of word2vec for syntax problems. In Proc. of NAACL.
[3] Mohit Bansal, Kevin Gimpel, Karen Livescu. 2014. Tailoring Continuous Word Representations for Dependency Parsing. ACL.
总结他们的思想,主要是将抽取好的 dependency relation 或者其他 relation 和 信息,表达成 modifier-relation/tag 的 pair,这个 pair 作为新的 context,替代原先 word2vec 中的 context 信息。
(2)bag-of-words
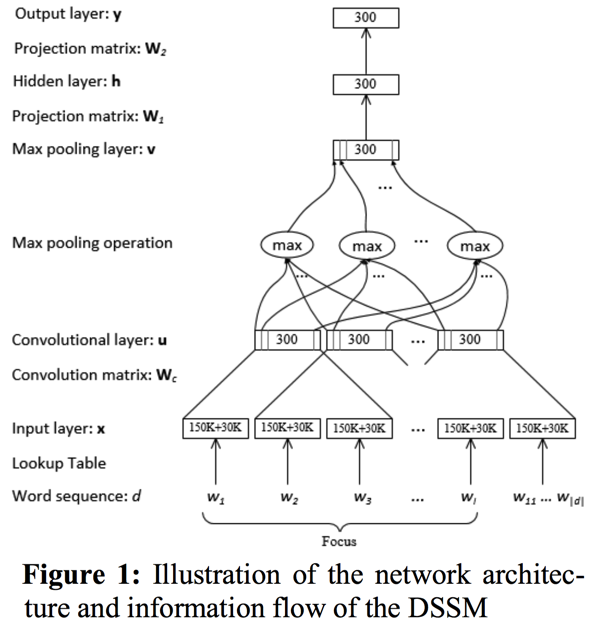
bag-of-words 可以说不仅有 non-order 的问题,还有 words 的问题。也就是说,现在的工作是基于 word/token level 去做的,但实际上已经有不少人质疑这点,认为 character-level 的信息足够可以当做 input 输入。对于 non-order 方面,有人提出了用多个 embedding matrix 来增强 word2vec 中的 同一个 embedding matrix,从而使得原始的 context 位置信息可以保留;而其实刚才上面 linear 增强部分提到的 dependency pair 的方法也可以看做是保留了 order。而,关于 word-level 的问题,很多人虽然考虑了 morpheme 层面的信息,但不能算是直接替代 word-level input;相反,MSR 的 Deep Learning 组,由 Jianfeng Gao 等人 lead 的 DSSM (Deep Structured Semantic Model or Deep Semantic Similarity Model)则提倡从 Sub-Word Unit (SWU)的层面进行输入。相关工作可见:
[4] Mikolov Tomáš, Sutskever Ilya, Deoras Anoop, Le Hai-Son, Kombrink Stefan, Černocký Jan. Subword Language Modeling with Neural Networks. Not published (rejected from ICASSP 2012).
[5] Omer Levy and Yoav Goldberg. 2014. Dependency based word embeddings. In Proceedings of ACL.
[6] MSR DSSM 系列:
[Huang, He, Gao, Deng, Acero, Heck, CIKM2013]
[Shen, He, Gao, Deng, Mesnil, WWW2014]
[Gao, He, Yih, Deng, ACL2014]
[Yih, He, Meek, ACL2014]
[Song, He, Gao, Deng, Shen, MSR-TR 2014]
[Gao, Pantel, Gamon, He, Deng, Shen, EMNLP2014]
[Shen, He, Gao, Deng, Mesnil, CIKM2014]
[He, Gao, Deng, ICASSP2014 Tutorial]
[Liu, Gao, He, NAACL2015] [Gao, He, Deng, MSR-TR-2015]
[7] Siyu Qiu, Qing Cui, Jiang Bian, Bin Gao, and Tie-Yan Liu. 2014. Co-learning of Word Representations and Morpheme Representations. COLING.
(3)contexts
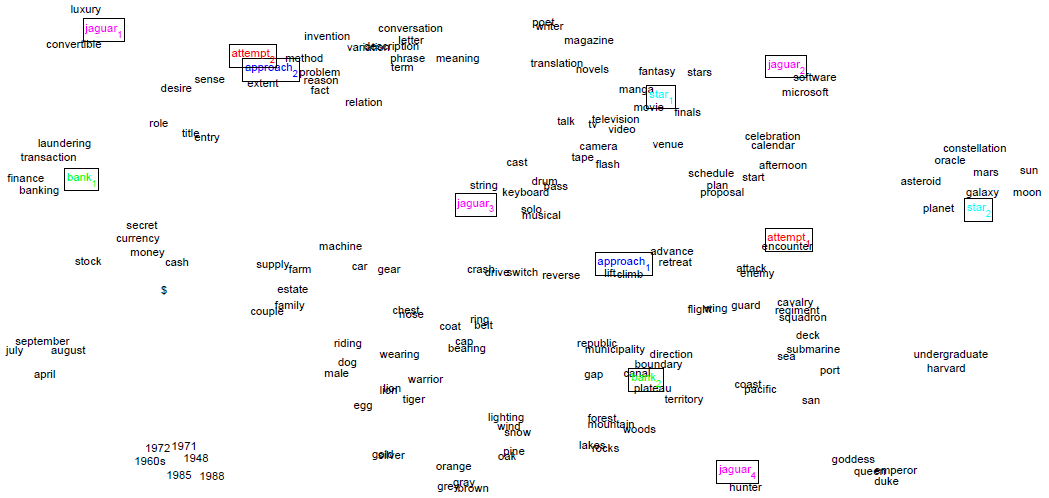
既然单纯的 context 可以认为是有用的,也可以被认为是不足的。除了固定 window size 内的上下文 contexts words 信息,还有什么可以用的信息呢?这样的考虑下,又带来了两种不同的改进。一种是直接替换掉 contexts words,用其他 enriched information words,比如 modifier-dependency-label pairs,比如 related word pairs(比如 WordNet 里那些 synonymy words)。另一种就是直接在 local contexts(即 window size 内的 context)的基础上,结合进 global contexts 或者其他 additional information。这种结合多数是线性 combine 进另一个神经网络,首创的就是 Huang et al., 2012 年的非常重要的论文。其他相关改变 contexts 的文章有:
[8] Eric H. Huang, Richard Socher, Christopher D. Manning, Andrew Y. Ng. 2012. Improving Word Representations via Global Context and Multiple Word Prototypes. ACL.
[9] Asli Celikyilmaz, Dilek Hakkani-Tur, Panupong Pasupat, and Ruhi Sarikaya. 2015. Enriching Word Embeddings Using Knowledge Graph for Semantic Tagging in Conversational Dialog Systems. AAAI.
[10] Mo Yu and Dredze. 2014. Improving Lexical Embeddings with Semantic Knowledge. ACL.
